Molarity - Video Tutorials & Practice Problems

Ever wonder how a mass amount such as moles can be converted into the volume amount of liters? Well, molarity serves as the bridge between moles and liters.
Molarity
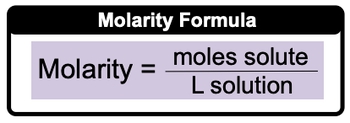
Molarity Example 1
Molarity
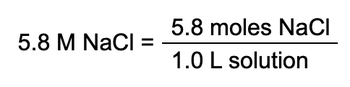
Molarity Example 2
What volume in (µL) of 0.125 M HBr contains 0.170 moles HBr?
Hypernatremia is a medical condition where a patient has high levels of sodium in their blood, and is the result of the body containing too little water. A patient has a measured sodium level of 165 mM. If 30.0 mL of their blood were drawn, what mass (in ng) of sodium would be present?
2.64 grams of an unknown compound was dissolved in water to yield 150 mL of solution. The concentration of the solution was 0.075 M. What was the molecular weight of the substance?
190 g/mol
30 g/mol
90 g/mol
240 g/mol
320 g/mol
A solution with a final volume of 750.0 mL was prepared by dissolving 30.00 mL of benzene (C6H6, density = 0.8787 g/mL) in dichloromethane. Calculate the molarity of benzene in the solution.
Do you want more practice?
- What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.19 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in enough water to pro...
- What is the molarity of Na+ in a solution of NaCl whose salinity is 5.6 if the solution has a density of 1.03 ...
- What is the molarity of each of the following solutions: (b) 5.25 g of Mn1NO322 # 2 H2O in 175 mL of solution,
- How many moles of solute are present in each of the following solutions? (b) 175 mL of 0.67 M glucose (C6H12O...
- How many moles of solute are present in each of the following solutions? (a) 35.0 mL of 1.200 M HNO3
- How many grams of solute would you use to prepare each of the following solutions? (b) 167 mL of 0.200 M boric...
- How many grams of solute would you use to prepare each of the following solutions? (a) 250.0 mL of 0.600 M eth...
- How many milliliters of a 0.45 M BaCl2 solution contain 15.0 g of BaCl2?
- How many milliliters of a 0.350 M KOH solution contain 0.0171 mol of KOH?
- The density of acetonitrile 1CH3CN2 is 0.786 g>mL and the density of methanol 1CH3OH2 is 0.791 g>mL. A s...
- The sterile saline solution used to rinse contact lenses can be made by dissolving 400 mg of NaCl in sterile w...
- The concentration of glucose (C6H12O6) in normal blood is approximately 90 mg per 100 mL. What is the molarity...
- An aqueous NaCl solution is made using 112 g of NaCl diluted to a total solution volume of 1.00 L. Calculate t...
- Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following solutions: (a) 255 mL of 1.50 M HNO31...
- An aqueous KNO3 solution is made using 72.5 g of KNO3 diluted to a total solution volume of 2.00 L. Calculate ...
- The estimated concentration of gold in the oceans is 1.0 * 10^-11 g/mL. (a) Express the concentration in mol/L...
- Calculate the molarity of each solution. c. 32.4 mg NaCl in 122.4 mL of solution
- Calculate the molarity of each solution. a. 3.25 mol of LiCl in 2.78 L solution
- How many grams of solute would you use to prepare the following solutions? (b) 1.50 L of 0.250 M glucose (C6H...
- How many grams of solute would you use to prepare the following solutions? (a) 500.0 mL of 1.25 M NaOH
- Describe how you would prepare each of the following aqueous solutions: (a) 1.50 L of 0.110 M 1NH422SO4 soluti...
- How would you prepare 500 mL of a 0.330 M solution of CaCl2 from solid CaCl2? Specify the glassware that shoul...
- How would you prepare 250 mL of a 0.100 M solution of fluoride ions from solid CaF2? Specify the glassware tha...
- Assuming that seawater is an aqueous solution of NaCl, what is its molarity? The density of seawater is 1.025 ...
- Commercial concentrated aqueous ammonia is 28% NH3 by mass and has a density of 0.90 g>mL. What is the mol...
- what is the molarity of Cl- in each solution? a. 0.200 M NaCl
- Brass is a substitutional alloy consisting of a solution of copper and zinc. A particular sample of red brass ...
- How many moles of KCl are contained in each solution? c. 114 mL of a 1.85 M KCl solution
- How many moles of KCl are contained in each solution? b. 1.8 L of a 0.85 M KCl solution
- How many moles of KCl are contained in each solution? a. 0.556 L of a 2.3 M KCl solution
- What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? c. 1.2 * 10 - 2 mol ethano...
- Propranolol 1C16H21NO22, a so-called beta-blocker that is used for treatment of high blood pressure, is effect...
- What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? b. 1.22 mol ethanol
- What volume of 0.200 M ethanol solution contains each amount in moles of ethanol? a. 0.45 mol ethanol
- Residues of the herbicide atrazine 1C8H14ClN52 in water can be detected at concentrations as low as 0.050 mg&g...
- (b) Can you identify which one between 0.10 mol ZnCl2 and 0.1M ZnCl2 contains more Zn2+ ion? Why?
- A laboratory procedure calls for making 400.0 mL of a 1.1 M NaNO3 solution. What mass of NaNO3 (in g) is neede...
- A chemist wants to make 5.5 L of a 0.300 M CaCl2 solution. What mass of CaCl2 (in g) should the chemist use?
- How would you prepare each of the following solutions? (a) A 0.150 M solution of glucose in water
- (c) How many milliliters of a 6.00 M NaOH solution are needed to provide 0.350 mol of NaOH?
- How would you prepare each of the following solutions? (b) 100 mL of an aqueous solution whose K+ concentratio...
- How would you prepare 165 mL of a 0.0268 M solution of benzoic acid 1C7H6O22 in chloroform 1CHCl32?
- (c) How many milliliters of 6.1 M HCl solution are needed to obtain 0.150 mol of HCl?
- (b) How many moles of KBr are present in 150 mL of a 0.112 M solution?
- How would you prepare 250 mL of a 0.325 M solution of benzoic acid 1C7H6O22 in chloroform 1CHCl32?
- A person suffering from hyponatremia has a sodium ion concentration in the blood of 0.118 M and a total blood ...
- Which of the following solutions is more concentrated? (a) 0.500 M KCl or 0.500 mass % KCl in water
- A solution is prepared by dissolving 20.2 mL of methanol (CH3OH) in 100.0 mL of water at 25 °C. The final volu...
- Household hydrogen peroxide is an aqueous solution containing 3.0% hydrogen peroxide by mass. What is the mol...
- The concentration of alcohol 1CH3CH2OH2 in blood, called the 'blood alcohol concentration' or BAC, is given in...
- One brand of laundry bleach is an aqueous solution containing 4.55% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) by mass. What ...
- (a) How many grams of ethanol, CH3CH2OH, should you dissolve in water to make 1.00 L of vodka (which is an aqu...
- The density of a 16.0 mass % solution of sulfuric acid in water is 1.1094 g/mL at 25.0 °C. What is the molarit...
- Ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, is the principal constituent of auto-mobile antifreeze. If the density of a 40.0 mass...
- medical lab is testing a new anticancer drug on cancer cells. The drug stock solution concentration is 1.5 * 1...
- Calicheamicin gamma-1, C55H74IN3O21S4, is one of the most potent antibiotics known: one molecule kills one ba...
- Pure acetic acid, known as glacial acetic acid, is a liquid with a density of 1.049 g/mL at 25 C. Calculate th...
- Bronze is a solid solution of Cu(s) and Sn(s); solutions of metals like this that are solids are called alloy...
- Neurotransmitters are molecules that are released by nerve cells to other cells in our bodies, and are needed...
- The density of a 20.0% by mass ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) solution in water is 1.03 g/mL. Find the molarity of t...
- Hard water contains Ca2+, Mg2+, and Fe2+, which interfere with the action of soap and leave an insoluble coati...
- Ammonium chloride, NH4Cl, is a very soluble salt in water. (c) If you dissolve 14 g of ammonium chloride in 5...
- In 2014, a major chemical leak at a facility in West Virginia released 28,390 L of MCHM (4-methylcyclohexylmet...
- Ritalin is the trade name of a drug, methylphenidate, used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder ...
- A railroad tank car derails and spills 36 tons of concen-trated sulfuric acid. The acid is 98.0 mass% H2SO4 an...
- Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 97.7 g LiBr in enough water to yield 750.0 mL of sol...
- What is the molarity of a solution that contains 17 g of NH3 in 0.50 L of solution?
- Commercial grade hcl solutions are typically 39.0% (by mass) hcl in water. Determine the molarity of the HCl, ...
- Find the molarity of a 40.0% by mass aqueous solution of sulfuric acid, H2SO4, for which the density is 1.305...
- A throat spray is 1.40% by mass phenol, C6H5OH, in water. If the solution has a density of 0.9956 g/mL, calcul...
- Which of the solutions have the same molar concentration as solution x?
- A solution of ethanol in water is prepared by dissolving 75ml
- Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 97.7 g LiBr in enough water to yield 750.0 ml of sol...
- How many moles of Ba(NO3)2 are there in 0.25 l of a 2.00 M Ba(NO3)2 solution?
- Volume (ml) of 2.25 M potassium hydroxide that contains 15.0 g of solute
- What is the molarity of a solution that contains 5.0 moles of solute in 2.0 liters of solution?
- Calculate the mass of ammonium sulfide (NH4)2S in 3.00 L of a 0.0200 M solution. g (NH4)2S
- What volume of 0.20 M NaCl(aq) contains 10.0 g of NaCl (molar mass 58 g/mol)?
- what volume of 0.220 m HBr solution (in mL) is required to obtain 0.0600 moles of HBr?
- Molarity is equal to ____________.
- How many moles of HCl are present in 0.70 L of a 0.33 M HCl solution?
- The amount of pure alcohol in a 1.25 oz. pour of 80-proof gin is
- What is the molarity of a solution containing 78.6 g of MgCl2 dissolved in 1.00 L of solution?
- What are the symbol and the name of the cation that makes up table salt?
- How many grams of AgCl would be needed to make a 4.0 M solution with a volume of 0.75 L?
- Alcohol strength refers to the ___________ in a beverage.
- What is the molarity of a solution that contains 125 g NaCl in 4.00 L solution?
- How many grams of sucrose (C12H22O11) are in 1.55 L of 0.758 m sucrose solution?
- How many moles of NaCl are present in 600 mL of a 1.55 M NaCl solution?
- How many moles of Cu(NO3)2 are in 2.35 L of a 2.0 M solution?
- What mass of MgBr2 in grams are in 215 mL of a 0.350 M solution of MgBr2?
- How many grams of LiF would be present in 575 mL of 0.750 M LiF solution?
- What is the molarity of a solution containing 4.2 moles of NaCl and a volume of 2.3 L?

