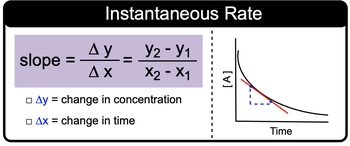
Instantaneous rate is the rate of a reaction at any particular point in time. And we're going to say here that calculated using the slope of the tangent line to the curve of that point is the way we obtain our instantaneous rate. So if we're given basically a plot of Y&X coordinates, we can use that to figure out the slope which will be equal to our instantaneous rate.
Now we're going to say while the rate of reaction decreases with time because the amount of reactant is decreasing in time. Instantaneous rate though remains constant here. If we take a look, we say that if we're given points Y&X, we can figure out the slope. Remember that slope is equal to changing Y over change in X rise over run. This really means Y2 - Y1X2 - X1.
Here we would change. We would keep the change in Y as changes in our concentration and our changes in X as changes in time. Now here we have the graphical representation of a curve and again we've used two points in terms of this which would relate to our tangent line. We'd utilize this formula for slope and use that to figure out our instantaneous rate.
So just keep this in mind as we start investigating more and more questions dealing with calculating the instantaneous rate of an overall reaction or at any particular point.